Assigned Reading on the Syntax of Expressions
This work is to be done before Exam 1.
Read Sections 2.1 and 2.2 on pp. 28 – 33 of Sethi (up to and including the figure at the top of p. 33).
A. Problems from Sethi
Do problems 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.7, and 2.8 on pp. 49 – 50 of Sethi.
Problem 2.1:
Rewrite the following expressions in prefix notation. Treat sqrt as an operator with one argument.
-
(a) $a\ *\ b\ +\ c$
Solution
+ * a b c -
(b) $a\ *\ (b\ +\ c)$
Solution
* a + b c -
(c) $a\ *\ b\ +\ c\ *\ d$
Solution
+ * a b * c d -
(d) $a\ *\ (b\ +\ c)\ *\ d$
Solution
* * a + b c d -
(e) $\frac{b/2\ +\ \sqrt{(b/2)\ *\ (b/2)\ -\ a\ *\ c}}{a}$
Solution
/ + / b 2 SQRT - * / b 2 / b 2 * a c a
Problem 2.2:
Rewrite the expressions of Exercise 2.1 in postfix notation
Solution
(a) a b * c +
(b) a b c + *
(c) a b * c d * +
(d) a b c + * d *
(e) b 2 / b 2 / b 2 / * a c * - SQRT + a /
Problem 2.3:
Draw abstract syntax trees for the expressions in Exercise 2.1
Solution
(a) Abstract Syntax Tree:
+
/ \
* c
/ \
a b
(b) Abstract Syntax Tree:
*
/ \
a +
/ \
b c
(c) Abstract Syntax Tree:
+
/ \
* *
/ \ / \
a b c d
(d) Abstract Syntax Tree:
*
/ \
* d
/ \
a +
/ \
b c
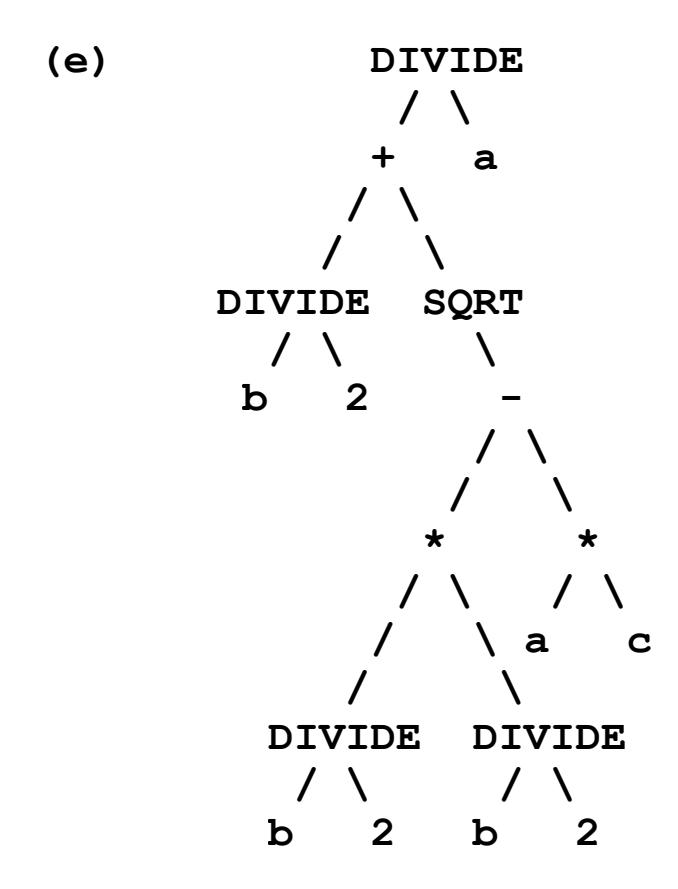
Problem 2.7:
Draw abstract syntax trees for the expressions in Exercise 2.6 (listed below):
-
(a) $2\ +\ 3$
-
(b) $(2\ +\ 3)$
-
(c) $2\ +\ 3\ *\ 5$
-
(d) $(2\ +\ 3)\ *\ 5$
-
(e) $2\ +\ (3\ *\ 5)$
Solution
(a,b) +
/ \
2 3
(c,e) +
/ \
2 *
/ \
3 5
(d) *
/ \
+ 5
/ \
2 3
Problem 2.8:
Postfix expressions can be evaluated with the help of the stack data structure, as follows:
- Scan the postfix notation from left to right.
- a. On seeing a constant, push it onto the stack.
- b. On seeing a binary operator, pop two values from the top of the stack, apply the operator to the values, and push the result back onto the stack.
- After the entire postfix notation is scanned, the value of the expression is on top of the stack.
Illustrate the use of a stack to evaluate the expression 7 7 * 4 2 * 3 * −.
Solution
Stack evaluation of 7 7 * 4 2 * 3 * -:
Stack Remaining Input
───────────── ──────────────────
7 7 * 4 2 * 3 * -
7 7 * 4 2 * 3 * -
7 7 * 4 2 * 3 * -
49 4 2 * 3 * -
49 4 2 * 3 * -
49 4 2 * 3 * -
49 8 3 * -
49 8 3 * -
49 24 -
25
B. Infix, Prefix, and Postfix Syntax Exercises
Problem 1: Operator Precedence and Abstract Syntax Trees
In a certain language expressions are written in infix syntax. The language has binary, prefix, and postfix operators that belong to the following precedence classes:
| Precedence Class | Symbol | Binary Ops | Prefix Ops | Postfix Ops | Associativity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Class (highest) | # | ~ | ~ | [none] | right |
| 2nd Class | @ | [none] | [none] | $ | left |
| 3rd Class (lowest) | % | ^ | @ | [none] | right |
Problem 1(a): Say which operator is applied last in the following expression, and then draw the abstract syntax tree of the expression. [To help you, subscripts have been attached to each operator to indicate its precedence class and whether that class is left- or right-associative, even though this information can also be obtained from the above table.]
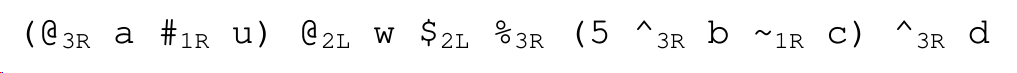
Solution
The operator % is applied last.
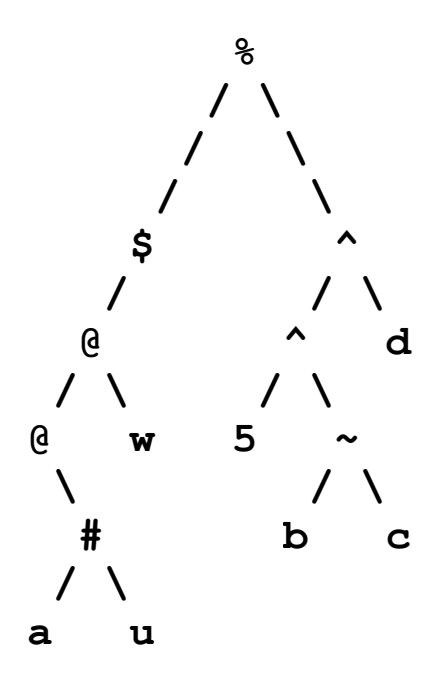
Problem 1(b): Rewrite the expression in prefix syntax.
Solution
% $ @ @ # a u w ^ ^ 5 ~ b c d
Problem 1(c): Rewrite the expression in postfix syntax.
Solution

a u # @ w @ $ 5 b c ~ ^ d ^ %
Problem 2: Postfix to Prefix Conversion
Draw the AST of the following postfix syntax expression, and rewrite the expression in prefix syntax. A subscript has been attached to each operator that shows the operator’s arity. [The operators in this question and the next are not related to the operators in question 1.]

Solution
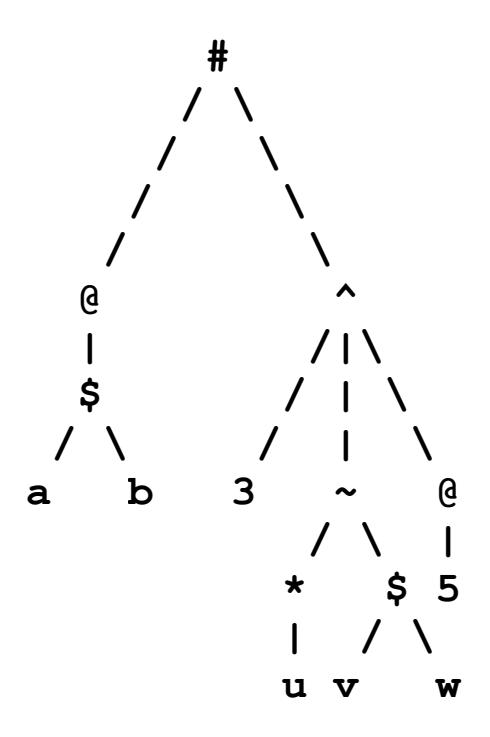
Prefix syntax:
# @ $ a b ^ 3 ~ * u $ v w @ 5
Problem 3: Prefix to Postfix Conversion
Draw the AST of the following prefix syntax expression, and rewrite the expression in postfix syntax. A subscript has been attached to each operator that shows the operator’s arity.
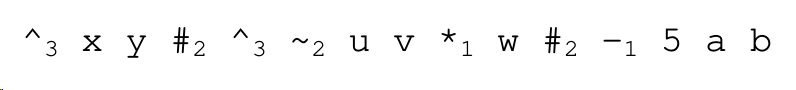
Solution
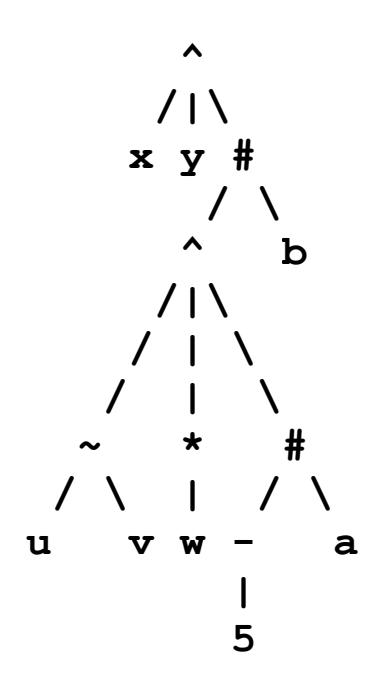
Postfix syntax:
x y u v ~ w * 5 a # ^ b # ^